Understanding the parsing process
Let's take a look at how the parsing process works in Lanat with argument types.
Here's a regular command structure with 4 arguments:

Parsing pipeline
Initial values reception
Once the input is tokenized, the parsing process begins. Lanat goes through the input and forwards the values specified on each argument to the proper sub-parsers, which are the argument types.
An argument may appear more than once in the input, and each time it appears, the argument type will receive the values.
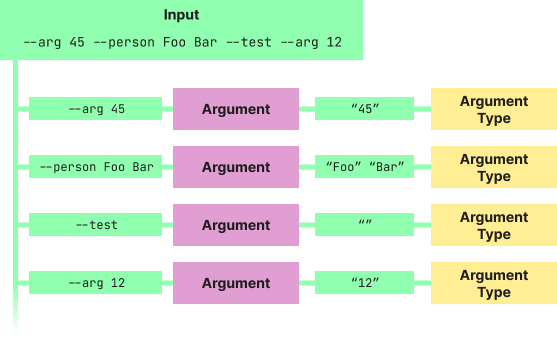
The "sanitized" values that you can see between the Argument and Argument Type nodes are the values that the argument type instance will receive in the parameter of its parseValues method.
Error collection
When parsing the values received, the argument type may encounter errors with the input. These errors are collected and later shown to the user in a formatted form.

It is important to note that not only argument types can throw errors. For instance, when the input is first tokenized, any syntax errors will be thrown by the tokenizer and collected as well.
When parsing, there are some other kind of errors that can be thrown by the parser, such as when the user provides an incorrect number of values for an argument type. If this occurs, that argument type will never receive the values that caused the error, and the error will be collected and shown to the user.
The Lanat parser provides the extra layer of input sanitization that the argument types don't need to worry about.
Final values reception
Once all tokens are parsed, it is time to collect the final values from the argument types. The argument types at this point likely have already parsed values.
